Multiple heavyweight projects have been implemented; Egypt is becoming a hot spot for Chinese enterprise investment.
Release time:
2025-09-09 10:32
Source of text | Daily Business News
Reporter | Yang Yilin
This article is compiled from Zhejiang CCPIT and Caixin Media
Since the beginning of this year, Chinese companies have gradually increased their investment projects in Egypt, and Sino-Egyptian economic and trade relations are flourishing. The latest example is the tire production base project announced last week by Sailun Group.
As the first domestic tire company to build a factory overseas, Sailun Group announced on August 15 that it will invest $291 million in Egypt to build a "3.6 million radial tire annual production project," with a construction period of 18 months. The company expects a payback period of 6.15 years, targeting the local Egyptian and surrounding markets.
On August 13, Sailun Group signed an agreement with TEDA Egypt Company to build this large tire manufacturing plant in the China-Egypt TEDA Suez Economic and Trade Cooperation Zone in the Suez Canal Economic Zone (SCZone).

The chairman of the economic zone, Waleid Gamal El-Dien, said that this tire factory is the cornerstone of the special zone's plan to build an integrated automotive manufacturing industrial cluster.
Multiple heavyweight projects land in Egypt
Since the beginning of this year, Chinese companies have concentrated their overseas investment and construction in Egypt. Earlier this year, Arab Potash International announced an investment of up to $10 billion to build a large phosphate fertilizer industrial complex in Egypt, aiming to accelerate phosphate mining and fertilizer production.
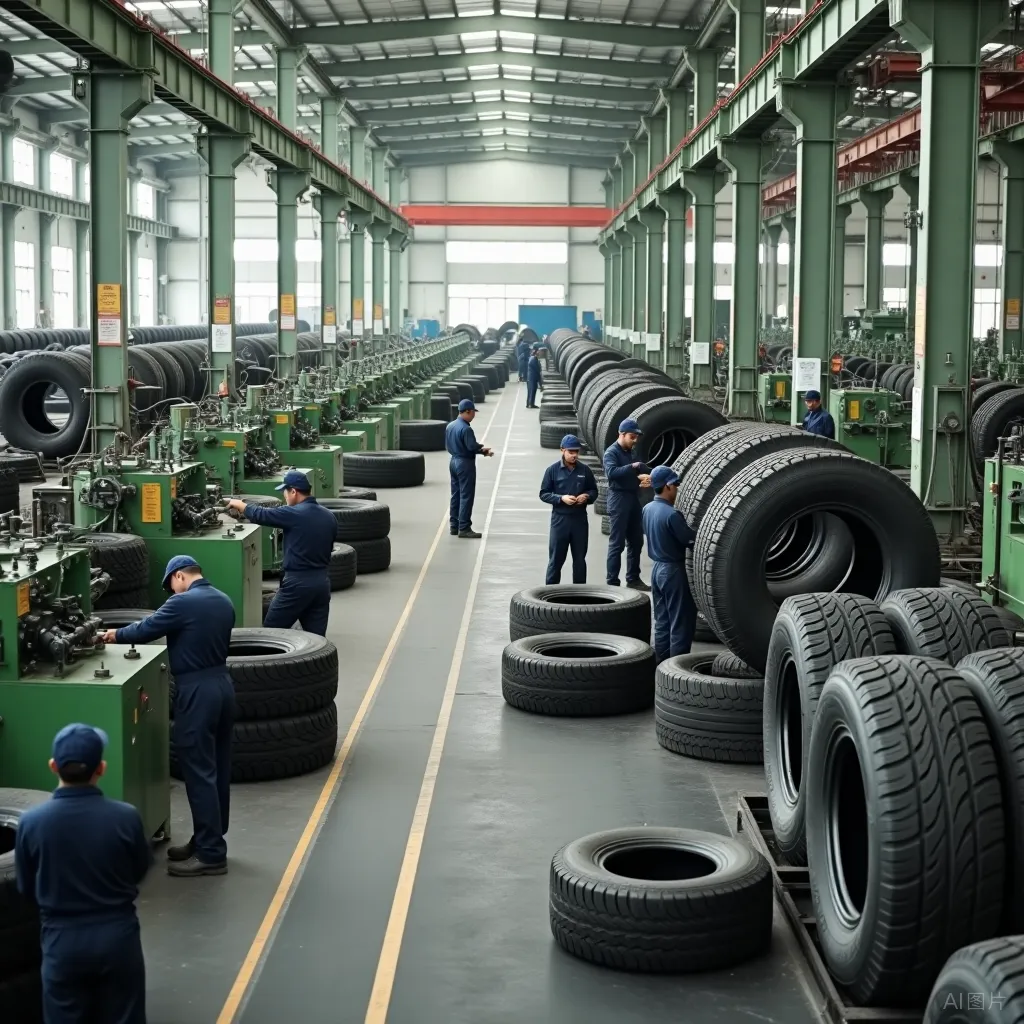
Zhejiang Caidi Industrial invested about $100 million to build a textile factory in the TEDA Cooperation Zone, which officially started production in February this year, becoming a core pillar of Egypt's industrial value addition. In March this year, Xinfeng Steel signed an agreement with the Suez Canal Economic Zone Authority to invest $1.65 billion to build a manufacturing center focused on end industrial products, targeting high value-added industries such as automobiles, construction machinery, and home appliances within the special zone.
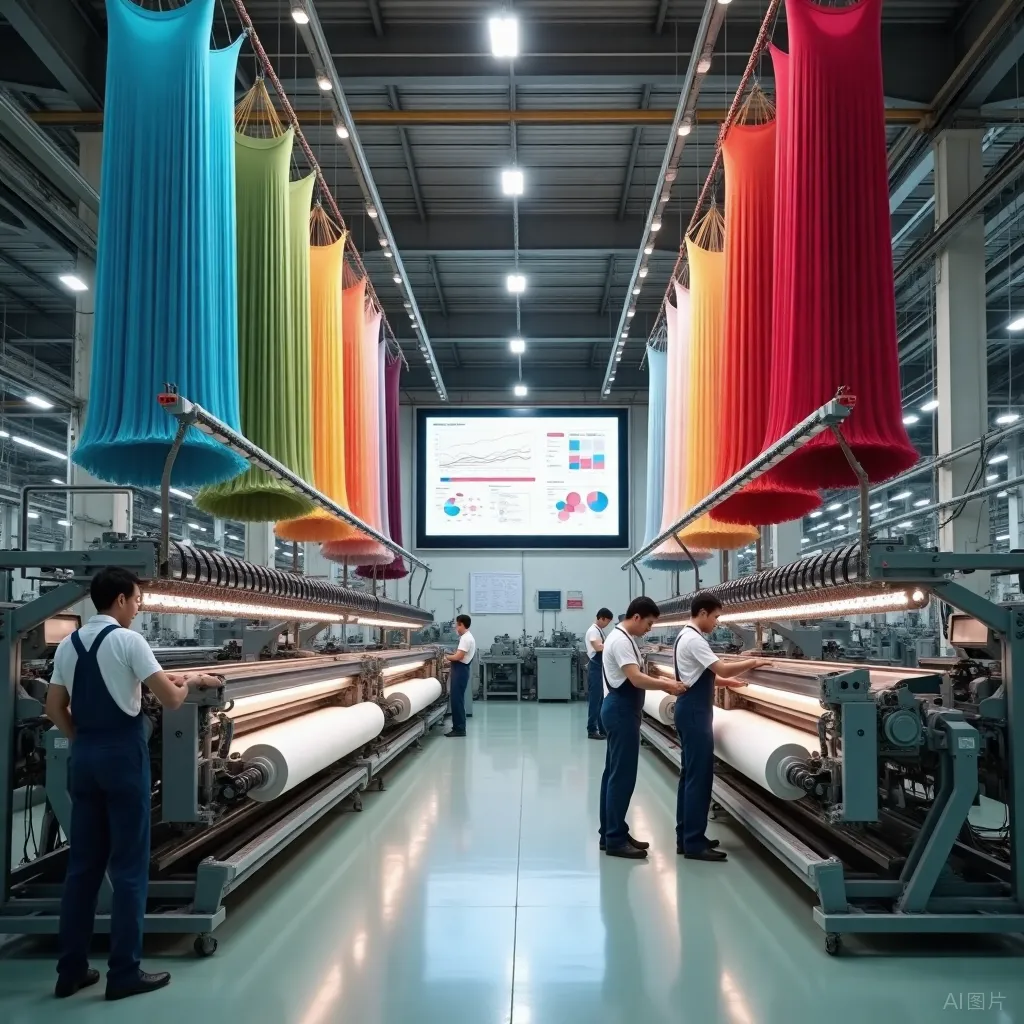

The Suez Canal Economic Zone is located near the Suez Canal, one of the world's busiest maritime trade routes. It consists of six ports and four industrial zones, covering 461 square kilometers, and enjoys special legal, fiscal, and regulatory incentive systems to attract foreign investment. The TEDA Cooperation Zone is jointly developed by Tianjin TEDA Holdings of China and the China-Africa Development Fund. Currently, more than 160 Chinese companies have settled in the TEDA Cooperation Zone, covering key fields such as electronics, electric vehicles, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy. The first phase covers 7.34 square kilometers, with plans to expand to 10 square kilometers.
According to data from the General Authority for Investment and Free Zones (GAFI) of Egypt, there are currently about 2,800 active Chinese companies in Egypt, with cumulative investments exceeding $8 billion. This number is expected to grow to $12 billion by the end of 2025.
Favorable conditions
The acceleration of Chinese investment in Egypt is partly due to the Egyptian government's opening of a direct RMB investment channel in April this year and the introduction of multiple preferential policies, creating unprecedented favorable conditions for Chinese companies investing in Egypt.
On the other hand, Egypt itself has unique geographical advantages. Located at the junction of Africa, Asia, and Europe, Egypt borders Europe to the north, connects to the African hinterland to the southwest, and adjoins West Asia to the east. It controls the Suez Canal, which handles 12% of global maritime trade volume, covering a consumer market of over 1.5 billion people in the surrounding region. Meanwhile, Egypt has joined multiple free trade agreements and preferential arrangements, with most exports to the EU, the US, Africa, and Middle Eastern countries enjoying zero or low tariffs.
Egypt also has abundant labor, huge market potential, and rich natural resources. It is the most populous country in the Arab world, with a high proportion of young people, and its local consumption structure is undergoing an upgrade process.
In recent years, China and Egypt have cooperated extensively in infrastructure, energy, technology, and finance, deepening their partnership based on China's "Belt and Road" initiative and Egypt's "Vision 2030." Chinese companies have played key roles in projects such as the Benban Solar Park (the world's largest solar power station), the Egypt Iconic Tower, and the Central Business District of the New Administrative Capital, highlighting China's important position in Egypt's urbanization and infrastructure development.
Additionally, cooperation in the transportation sector is continuously advancing. Chinese companies are involved in a $10 billion electric train project and a high-speed rail network connecting Cairo with other major cities. These projects not only help Egypt modernize its internal connectivity but also strengthen its position as an international regional trade and manufacturing hub.
Financial cooperation between the two sides is also deepening. In July this year, the People's Bank of China and the Central Bank of Egypt signed multiple memorandums of understanding aimed at enhancing financial integration, covering local currency settlement, currency swaps, technical cooperation, and panda bond issuance.
Frequent high-level visits throughout 2025 lay the foundation for deeper strategic cooperation between China and Egypt in defense, education, industry, and technology. It is expected that these collaborations will reach new heights in 2026, when China and Egypt celebrate the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations.
—END—
Related News
2025-11-28